This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before considering any peptide therapy.
Peptides offer a regenerative approach to hair restoration by targeting follicle stem cells, growth factor production, and cellular signaling pathways that control the hair growth cycle, with clinical studies showing measurable improvements in hair density and reduced shedding.
Quick Takeaways
- Copper peptides (GHK-Cu) increase hair density by approximately 27% after six months through growth factor stimulation and improved blood flow
- Biotinoyl tripeptide-1 reduces hair loss by 58% and increases density by 35% through reinforcing the extracellular matrix around follicles
- Peptides demonstrate better tolerability than conventional treatments, with most side effects limited to mild, temporary scalp irritation
- Combination approaches pairing peptides with microneedling or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy show superior outcomes compared to single-modality treatments
Understanding Peptides and Hair Restoration
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that act as signaling molecules in the body. When applied topically or injected into the scalp, specific peptides can stimulate dormant hair follicles, extend the active growth phase, and strengthen the structural proteins that anchor hair in place.
Traditional hair loss treatments like minoxidil and finasteride work through secondary mechanisms—vasodilation and hormone blocking, respectively. Peptides take a different approach by directly influencing the biological processes that govern follicle cycling, making them an attractive option for people seeking alternatives to pharmaceutical interventions or looking to enhance existing treatment protocols.
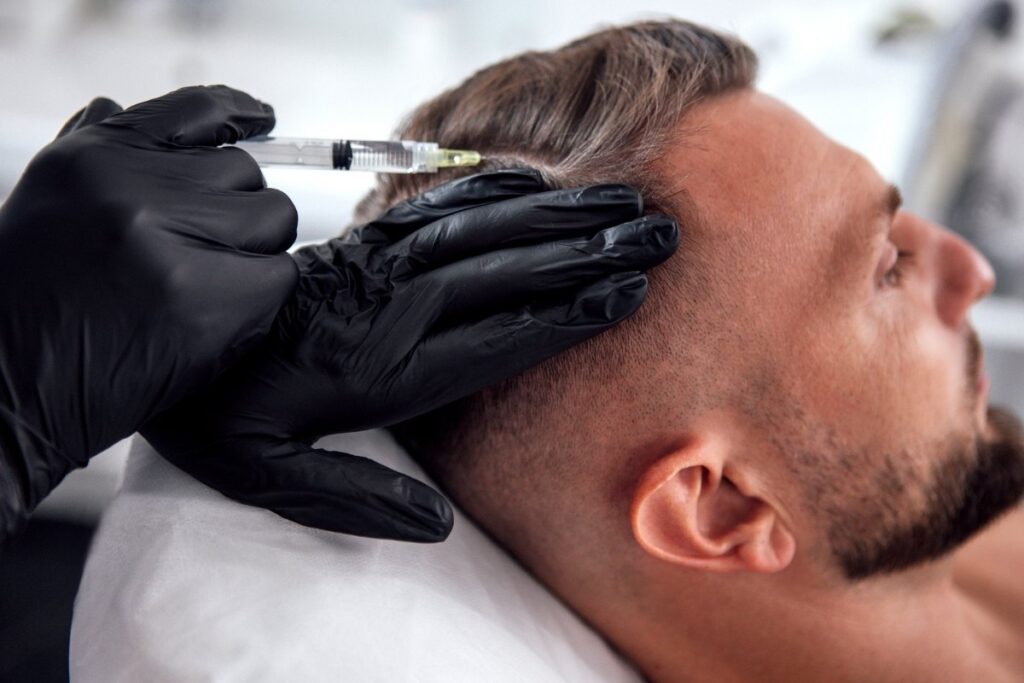
How Peptides Promote Hair Growth
Activating Hair Follicle Stem Cells
Health growth is regulated through a multifaceted complex of vascular, endocrine and neural stimuli, each of which are influenced by age or nutrient intake. The hair growth cycle is divided into 3 key phases:
- 1. Anagen phase (growth) were follicle stem cells grow rapidly to form keratinocytes that develop the hair shaft,
- 2. Catagen phase (transition) where the follicle undergoes apoptosis-driven regression, reduced shaft diameter and subsequent shedding
- 3. Telogen phase (rest) where stem cells are in a dormant stage and growth does not occur.
Hair follicles contain stem cell populations in the bulge region that remain dormant during the resting phase. Peptides like acetyl tetrapeptide-3 activate these stem cells by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which controls the transition from telogen (resting) to anagen (growth) phases.
When β-catenin accumulates in stem cells, it binds to Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1/T cell factor 3 (LEF1/TCF3) transcription factors and triggers expression of genes including c-Myc and cyclin D1. This cascade prompts stem cells to proliferate and differentiate into the specialized cells needed for hair shaft production.
The novel molecule PP405 takes this mechanism further by inhibiting proteins, such as the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC), which keeps stem cells dormant. In a phase 2a trial, 31% of men with advanced hair loss who received PP405 experienced more than 20% increase in hair density at eight weeks—a response rate far exceeding placebo controls.
Stimulating Growth Factor Production
Several peptides work by boosting production of growth factors that support follicle function. GHK-Cu increases expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), both of which promote blood vessel formation and nutrient delivery to follicles.
Collagen-derived peptides stimulate dermal papilla cells—specialized cells at the follicle base—to secrete insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 (IGFBP-6), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and additional VEGF. These growth factors create a microenvironment that supports follicle elongation and hair shaft development.
Research using AP collagen peptides demonstrate enhanced phosphorylation of Akt, GSK-3β, and β-catenin proteins, confirming activation of the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway central to follicle regeneration. This signaling cascade promotes new hair shaft induction in both laboratory tissue samples and live animal models.
Strengthening the Extracellular Matrix
The extracellular matrix provides structural scaffolding that anchors hair follicles in the dermis. Peptides like acetyl tetrapeptide-3 and biotinoyl tripeptide-1 increase production of collagen, laminin, and other matrix proteins that reinforce this anchoring system.
Stronger follicle anchoring reduces premature shedding during the telogen phase. Clinical trials of acetyl tetrapeptide-3 documented a 67% increase in hair growth activity and 17% increase in hair diameter, likely reflecting both improved anchoring and enhanced follicle function.
Biotinoyl tripeptide-1 combines a biotin molecule with a tripeptide sequence, delivering both structural support and direct stimulation of keratinocyte proliferation. This dual mechanism explains its impressive 58% reduction in hair loss observed in controlled studies.
Third-Party Tested, 99% Purity
Order lab-verified peptides from our top recommended vendor.

Clinical Evidence for Specific Peptides
Copper Peptides: GHK-Cu
A study using a thermodynamically stable microemulsion delivery system for GHK-Cu found that treated hair follicles entered early growth stages in six days, compared to eight days for standard copper peptide formulations and nine days for minoxidil. The enhanced delivery system increased VEGF and HGF secretion more substantially than conventional preparations.
Gene expression analysis confirmed that GHK-Cu upregulated Wnt10b and β-catenin while also increasing lactate dehydrogenase expression. Lactate production serves as a metabolic signal that activates hair follicle stem cells, providing another pathway through which copper peptides promote hair growth.
A six-month clinical trial reported 27% increase in hair density among users applying copper peptide serum daily. Participants also noted reduced shedding, suggesting that GHK-Cu helps retain existing hair while promoting new growth.
Biotinoyl Tripeptide-1 and Acetyl Tetrapeptide-3
A randomized controlled trial compared an herbal extract combination containing acetyl tetrapeptide-3 and biochanin A against 3% minoxidil solution. After 24 weeks, both groups showed similar improvements in terminal hair counts—8.3% for the peptide combination versus 8.7% for minoxidil—with no statistical difference between treatments.
Similarly, both the herbal extract combination containing acetyl tetrapeptide-3 and biochanin A and 3% minoxidil solution treatments were well-tolerated. These results suggest the herbal extract combination containing acetyl tetrapeptide-3 and biochanin A provides an effective, alternative option for patients desiring to take a more naturopathic approach.
Standardized phototrichography assessment of biotinoyl tripeptide-1 confirmed a 35% increase in hair density and 58% reduction in hair loss after three months of twice-daily application. Users reported improvements in hair thickness, volume, and overall appearance.
Collagen Peptides for Follicle Support
A study examining AP collagen peptides found they increased proliferation of both dermal papilla cells and outer root sheath cells while stimulating secretion of multiple growth factors. In mouse models, collagen peptide treatment promoted earlier transition from telogen to anagen and prolonged the active growth phase.
The peptides improved hair thickness and amino acid content, particularly cystine and methionine—sulfur-containing amino acids critical for keratin cross-linking. Analysis confirmed upregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and downregulation of BMP signaling, which normally inhibits follicle activation.
A clinical trial of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation for telogen effluvium showed the percentage of hairs in anagen phase increased from 67.92% at baseline to 71.52% at 16 weeks with drinkable collagen, and from 68.63% to 75.68% with tablet formulation. Combination treatment yielded the highest improvement in anagen phase percentage.
Comparing Peptides for Hair Growth
| Peptide | Mechanism | Key Benefits | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| GHK-Cu | Growth factor stimulation, angiogenesis, Wnt pathway activation | 27% density increase, reduced shedding | Topical serum or injectable |
| Biotinoyl Tripeptide-1 | Keratin production, matrix reinforcement | 58% less hair loss, 35% more density | Topical serum |
| Acetyl Tetrapeptide-3 | Matrix strengthening, follicle anchoring | 67% growth activity boost, 17% thicker diameter | Topical formulation |
| AP Collagen Peptides | Dermal papilla stimulation, growth factor secretion | Extended anagen phase, improved amino acid content | Oral supplement |
Treatment Protocols and Administration
Topical Application Methods
Most peptide serums are applied twice daily to clean, dry scalp. Start with a small amount—typically 1 to 2 milliliters—and massage gently into areas of thinning or loss. Allow the product to absorb for several minutes before applying other styling products.
Results typically appear after 8 to 12 weeks of consistent use, with maximum benefits seen around the six-month mark. Early shedding during the first few weeks can be viewed as a concern, however, this often represents a positive treatment response as follicles transition from a resting to growth phase.
Microneedling enhances peptide penetration by creating microchannels in the scalp. Use a dermaroller with 0.5 to 1.5 millimeter needles once weekly, with application of a peptide serum immediately afterward. This combinatorial approach can accelerate results by improving bioavailability.
Injectable Peptide Protocols
Injectable peptides deliver higher concentrations directly to follicle tissue. GHK-Cu is typically administered at 0.1 milliliter daily via shallow subcutaneous injection into the scalp. Some practitioners use mesotherapy techniques to distribute peptides across treatment areas.
A recent study examined monthly sessions of minoxidil-dutasteride-copper peptide tattooing (microinfusion via tattooing technique) in seven men with androgenetic alopecia. After five treatments, the median top-quadrant hair coverage improved from 40% baldness to 7.5% baldness. Five patients achieved greater than 10% regrowth, with median regrowth of 26.5%.
No adverse reactions including scarring or infection occurred, demonstrating the safety of properly administered injectable peptide protocols. The combination approach outperformed previous results with minoxidil-dutasteride alone, suggesting copper peptides provided synergistic benefits.
Combination Strategies
Pairing peptides with complementary therapies often produces superior outcomes. PRP injections deliver autologous growth factors while peptides provide sustained signaling support. Low-level laser therapy improves scalp circulation, potentially enhancing peptide uptake.
Oral collagen peptides supply systemic amino acid support for keratin synthesis while topical peptide serums target local follicle activation. A 16-week study found combination oral collagen supplementation produced greater improvements in anagen phase percentage than either formulation alone.
Nutritional optimization supporting peptide therapy includes adequate protein intake (1.2 to 1.6 grams per kilogram body weight), biotin supplementation, and minerals including zinc and iron. These nutrients provide the raw materials follicles need to respond to peptide signaling.

Safety and Contraindications
Common Side Effects
Peptides demonstrate favorable safety profiles compared to pharmaceutical hair loss treatments. Most users experience no adverse effects, while a small percentage report mild scalp irritation, redness, or itching during initial applications. These reactions typically resolve within one to two weeks as the scalp adapts.
Temporary increased shedding during the first month reflects follicle cycling rather than treatment failure. As dormant follicles activate and enter growth phases, they first shed any existing telogen hairs. New growth follows within several weeks.
Injectable peptides may cause minor injection site reactions including tenderness, swelling, or bruising. These effects are generally mild and resolve within days without intervention.
Contraindications and Precautions
People with active scalp conditions including psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or folliculitis should resolve these issues before starting peptide treatments. Applying peptides to inflamed or infected tissue may worsen symptoms.
Pregnant and nursing women should avoid peptide therapies due to insufficient safety data in these populations. While peptides are generally well-tolerated, their effects on fetal development and breast milk composition remain unknown.
Individuals with current or previous cancer should consult oncologists before using growth factor-promoting peptides. While theoretical concerns exist about stimulating malignant cell growth, clinical evidence of this risk remains limited because long-term studies in large populations have not been conducted.
Quality and Sourcing Considerations
Purchase peptides only from verified suppliers providing third-party testing certificates. Pharmaceutical-grade peptides ensure proper purity and reduce contamination risks that could cause adverse reactions or diminished efficacy.
Store peptide products according to manufacturer guidelines, typically in cool, dark locations away from moisture. Improper storage degrades peptide structure and reduces biological activity. Discard products past their expiration dates.
Frequently Asked Questions: Peptides for Hair Growth
How long before peptides show visible hair growth results?
Most people notice initial improvements around 8 to 12 weeks, with maximum benefits appearing at six months. Hair growth follows a slow biological timeline—follicles must transition through complete cycles before density changes become apparent. Consistent application throughout this period is necessary for optimal outcomes.
Can peptides help with androgenetic alopecia or only temporary hair loss?
Clinical studies demonstrate peptide efficacy for both androgenetic alopecia and telogen effluvium. GHK-Cu may help reduce dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels while simultaneously promoting follicle activation through growth factor pathways. However, combining peptides with DHT-blocking treatments like finasteride often produces better results for pattern baldness than peptides alone.
Are peptide results permanent or do they require ongoing treatment?
Peptide benefits depend on continued use. Stopping treatment typically results in gradual return to baseline hair density over several months as follicles revert to their genetically programmed behavior. Maintenance protocols with reduced frequency may sustain results while minimizing cost and application burden.
Can I use peptides with minoxidil or finasteride simultaneously?
Peptides combine safely with traditional treatments and may enhance their effectiveness. A study of combination minoxidil-finasteride therapy showed superior outcomes compared to monotherapy, and adding peptides to this foundation addresses hair loss through additional mechanisms. Consult a healthcare provider to design an integrated protocol appropriate for your specific situation.
References
- Acetyl tetrapeptide-3 vs minoxidil trial – Randomized controlled trial comparing herbal extract with acetyl tetrapeptide-3 against 3% minoxidil showing comparable efficacy with superior tolerability. An Herbal Extract Combination – PMC
- GHK-Cu mechanisms and regenerative actions – Review of copper peptide’s ability to increase hair growth, follicle size, and collagen production. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide – PMC
- PP405 phase 2a clinical trial results – Study showing 31% of men with advanced hair loss achieved >20% increase in hair density at 8 weeks compared to 0% with placebo. Pelage’s PP405 Demonstrates Efficacy in Phase 2a Trial – Dermatology Times
- Collagen supplementation for telogen effluvium – Clinical trial demonstrating increased anagen phase percentage from 67.92% to 71.52% with drinkable collagen and 68.63% to 75.68% with tablets. Targeted Nutritional Supplementation for Telogen Effluvium – PMC
- Minoxidil-dutasteride-copper peptide tattooing study – Research showing five monthly sessions improved median hair coverage from 40% baldness to 7.5% baldness with 26.5% median regrowth. Enhanced hair regrowth with minoxidil-dutasteride-copper peptides tattooing – PubMed
- GHK-Cu microemulsion delivery system – Study demonstrating thermodynamically stable microemulsion accelerated follicle entry into growth phase compared to standard formulations and minoxidil. Thermodynamically stable ionic liquid microemulsions – PMC







