[Disclaimer: The content in this article is solely for informational purposes and does not substitute medical diagnosis, advice, or treatment. Always consult a medical specialist before using any peptide.]
Is arthritis disrupting your mobility and everyday activities? Do you often find yourself longing to live a life free of joint stiffness and pain?
Well, if your answer is yes — you are not alone in the battle.
Most people develop arthritis between the ages of 30 and 60. As we age, our joints experience wear and tear, and the damage keeps getting worse.
Most patients are bound to take over-the-counter drugs. But using drugs in the long run causes more harm than good.
That’s where peptides show their magic for arthritis.
In this article, we will walk you through the action mechanism of peptides for arthritis, their key benefits, and the specific peptides for various arthritis conditions.
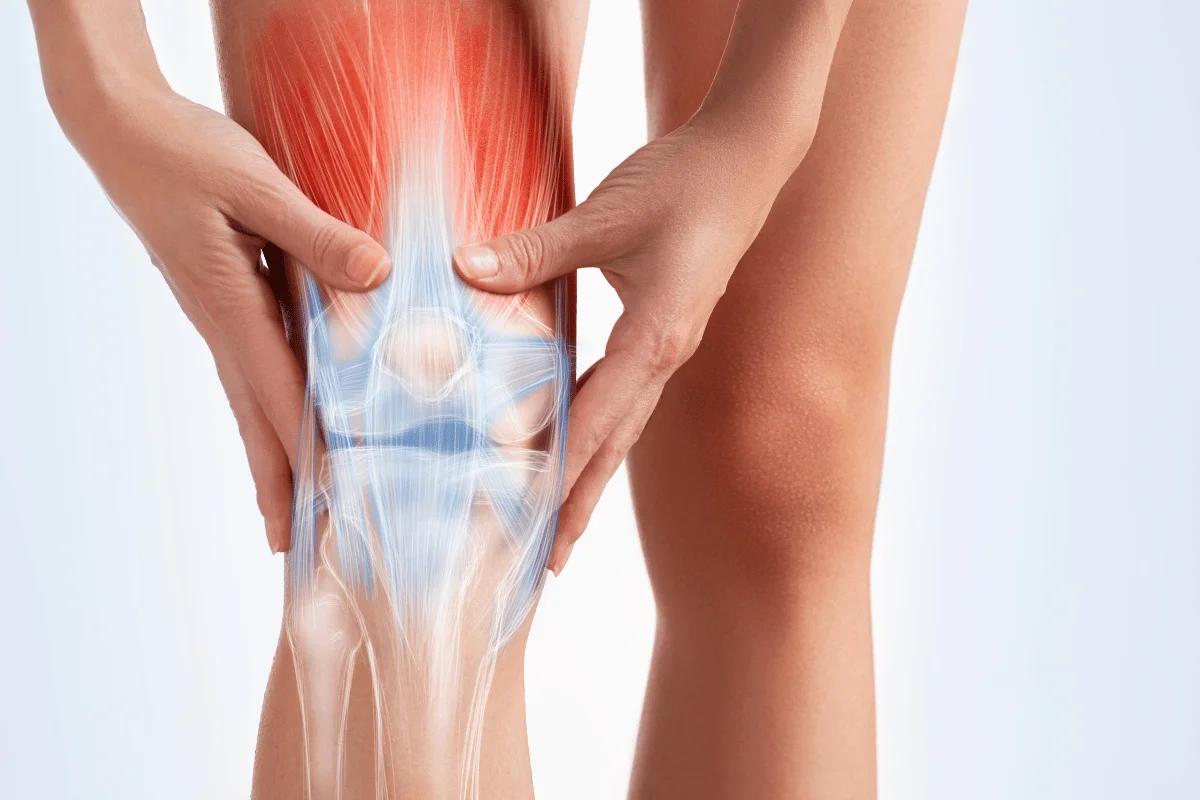
How Peptides Work for Arthritis?
Arthritis causes pain, inflammation (swelling), and joint stiffness due to aging, injury, or certain health conditions. It mainly affects the joints of the knees, hands and wrists, lower back, hips, and shoulders.
Peptides are the small chains of amino acids that treat inflamed joints by activating the body’s own healing system. They influence the inflammatory pathways in arthritis affectees to reduce joint inflammation and pain.
But that’s not all; peptides can also repair cartilage. Cartilage is flexible but firm tissue that provides cushioning between bones. Arthritis causes cartilage to wear and tear. Peptides not only repair cartilage but also stimulate its regeneration, providing relief from arthritis.
In short, peptides may treat arthritis and improve joint function by reducing pain, inflammation, and cartilage degeneration.
Benefits of Peptides for Arthritis
Peptides show tons of benefits for arthritis patients, as shown below:
Promotes Joint Repair by Forming Blood Vessels
Some peptides encourage the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). The increased blood flow supplies sufficient healing factors, nutrients, and oxygen to damaged tissues.
So, peptides are effective for arthritis management as they heal damaged tendons, bones, cartilage, and joints by forming blood vessels.
Fact: Even bodybuilders looking for the best peptides for bodybuilding prefer peptides (like TB-500 and BPC-157) for their tissue-repairing tendency.
Reduces Pain by Anti-inflammatory Activity
Peptides regulate the anti-inflammatory process to heal joints and reduce swelling, making daily joint movements pain-free.
Some peptides suppress the production of inflammatory proteins (cytokines) to prevent excessive inflammation and encourage neutrophils (immune cells) to penetrate joints.

Increases Joint Mobility by Collagen Synthesis
Collagen peptides promote the synthesis of collagen, which rebuilds tissue structure. Once inside the body, these peptides are fragmented into smaller chunks. The body absorbs and utilizes these chunks to strengthen and fix joint cartilage.
Collagen also contributes to the restoration of flexibility and stability in tendons and joints and helps them withstand stretching. It also strengthens joint tissues, preventing future injuries.
Enhances Bone Density by Osteoblasts
Peptides enhance bone density by improving the function of bone-building cells (osteoblasts). They also regulate the activity of the cells that degenerate the damaged bone tissues (osteoclasts). Degeneration of damaged tissues makes space for bone-building cells to repair and strengthen bones.
Additionally, peptides prevent fracture risk by improving bone support to the joints. For example, peptides for anti-aging, like GHK-Cu, strengthen bones in aging individuals.
Improves Joint Health by Stimulating hGH Synthesis
Peptides can improve joint health and treat arthritis symptoms by stimulating the synthesis of human growth hormone (hGH). hGH helps replace damaged tissues with healthy cells to strengthen joints.
Peptides maintain healthy levels of hGH to help the body regenerate and repair naturally and reduce stiffness and pain in arthritis by strengthening the cartilage and connective tissues.

Best Peptides for Arthritis
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), there are approximately 100+ types of arthritis. Multiple research studies show that peptides have promising effects against these types of arthritis.
Let’s look at a few of the top peptides for arthritis:
P90578
P90578 is a collagen-derived erythropoietin peptide. In a pre-clinical study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, P90578 reduced arthritis in the mice by:
- Reducing inflammation in upper and lower limb joints.
- Reducing autoantibody levels.
- Blocking the autoantibodies binding to autoantigens.
- Keeping cartilage intact.
Being an erythropoietin peptide, it might hold the risk of increasing RBCs. Therefore, it should only be used after doctor’s advice.
BPC-157 for Arthritis Relief
Due to the inflammation-reducing potential, BPC-157 (aka gastric pentadecapeptide) could be useful for arthritis. It supplies fibroblasts to repair tissues like ligaments and tendons. That’s why it is considered one of the best peptides for tendon repair.
It is also known to enhance the formation of new blood vessels and makes one of the best peptides for muscle growth. In a study, BP-157 injections were provided to patients with knee pain, where it showed:
- Reduced knee pain.
- Enhanced joint function.
BP-157 injections also showed promising results when used in combination with TB-500 peptide.
Peptides for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly affects healthy joints. If the disorder continues to grow at the same pace, there will be 31.7 million individuals with RA by 2050.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes pain, inflammation, stiffness, tenderness, and swelling in joints, cartilage, and surrounding tissues. It mostly affects small joints of the hands, wrists, fingers, feet, and toes.
Here are some peptides that may help with RA:
ARA-290
ARA290 is derived from a hormone (erythropoietin) that stimulates red blood cell (RBC) production. However, the good thing is that ARA-290 does not involve the risk of increasing RBC count. According to a clinical study published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, ARA290 was found to be effective in rheumatoid arthritis patients by:
- Decreasing the generation of pro-inflammatory agents.
- Increasing the generation of anti-inflammatory agents.
- Increasing production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
- Enhancing tissue repair.
- Decreasing inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
AESIS-1
AESIS-1 is a synthetic peptide that might be used to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. It works like disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) that mitigate the body’s immune response to treat arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
In mice, AESIS-1:
- Shows advanced wound repair by enhancing the movement of repairing factors (fibroblasts).
- Suppresses rheumatoid arthritis by reducing cartilage degradation and synovial inflammation.
Synovial inflammation occurs in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. It affects the synovial membrane that lines the joints and generates synovial fluid to provide lubrication.

Peptides for Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a progressive, autoimmune, and musculoskeletal disorder that affects 0.1%- 1% of individuals and approximately 20% of psoriasis patients. It causes inflammation in joints and at the attachment points of bones with ligaments and tendons (called entheses).
In psoriasis, the immune system becomes hyperactive. Most people get psoriasis before psoriatic arthritis, which is caused 7-10 years after the onset of psoriatic skin symptoms. Psoriatic arthritis is characterized by swollen toes and fingers, back pain, eye inflammation, and foot pain.
Here are some peptides that may help alleviate the condition:
SSPs
Small spleen peptides (SSPs) are natural peptides isolated from murine, porcine, and bovine spleens. SSPs have systemic effects, so they don’t necessarily need to be injected directly into the affected site. SSPs inhibited psoriatic arthritis in mice by:
- Calming the hyperactive immune cells (dendrites).
- Increasing the inflammation-controlling cells called T regulatory cells (Tregs).
Thymosin Alpha-1
Thymosin alpha-1 (Ta1) is found in the human thymus. Its synthetic form has immune-modulating effects and multiple clinical benefits, which is why it is approved for use in 35 countries.
Thymosin alpha-1 may attenuate psoriatic arthritis as it:
- Regulates a kind of white blood cells (called T cells).
- Prevents immune cells from attacking the healthy joint tissues.
Thymosin alpha-1 levels are significantly low in autoimmune conditions like psoriatic arthritis. Regulating its level aids in mediating antibody responses and T cells, ultimately reducing inflammation.
Peptides for Joint Inflammation
Joint inflammation leads to pain and swelling in any joint. It is most common in the knees, hips, or fingers. It can be caused by inflammatory arthritis, bursitis, or bacterial arthritis.
A few peptides that may be beneficial include:
Scolopendrasin IX
Ancient Chinese people used Chinese red-headed centipedes to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Researchers extracted an antimicrobial peptide (scolopendrasin IX) from this centipede and checked its effect on mice.
In mice, scolopendrasin IX alleviated joint pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis by:
- Suppressing synthesis of inflammatory agents (cytokines).
- Targeting a receptor (FPR2) present in immune cells.
- Activating the infection-fighting blood cells called neutrophils.
- Aiding the entry of neutrophils into the joints.
Collagen Hydrolysate
According to the Arthritis Foundation, collagen supplements are effective for arthritis patients. Collagen hydrolysate (aka hydrolyzed collagen) is a collagen peptide that gets absorbed in the body easily.
In a meta-analysis, collagen peptide was given to 507 knee osteoarthritis patients.
The peptide:
- Relieved their arthritic pain.
- Reduced joint inflammation.
Collagen peptides are among the best types of peptides for muscle growth, as they enhance muscle repair and synthesize muscle proteins.
Peptides for Knee Arthritis
In knee arthritis (aka osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease), the knee joint specifically gets inflamed.
These peptides may aid in mitigating the condition:
VIP
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is a neuropeptide with anti-inflammatory and immunity-modulating properties. VIP could be used as a peptide for osteoarthritis as it relieved osteoarthritis and pain in the knee joints of the rats.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disorder in which cartilage lining your joints wears down, making the bones rub against each other.
To alleviate this condition, VIP:
- Inhibits the inflammation-stimulating (NF-κB) pathway.
- Enhances the structural protein of cartilages (aka collagen II) to strengthen it.
However, its long-term intake may cause immunity problems and gastrointestinal issues.
AOD-9604
Last but not least, AOD-9604 regulates fat breakdown, tissue regeneration, and cell-repairing processes. It also promotes the production of collagen II – a key protein in cartilage and tendons. In rabbits with knee osteoarthritis, intra-articular injections of AOD-9604 alleviated knee osteoarthritis by:
- Improving cartilage regeneration.
- Reducing joint inflammation and pain.
Combining hyaluronic acid with AOD-9604 showed better results.
Fact: AOD-9604 is considered one of the best peptides for athletic performance due to its performance-enhancing effects. However, you must avoid it if you are in competitive sports.
How to Choose the Right Peptide for Arthritis
While choosing the right arthritis peptide, keep the following points in mind:
- Target Specificity: Choose the peptide that treats the specific arthritis condition you have.
- Clinical Evidence: Choose the peptides that have established efficacy and safety for humans.
- Administration Route: Understand the bioavailability and route of administration of peptides.
How to Use Peptide Injections for Arthritis
Peptides for arthritis are injected through the subcutaneous (skin) or intramuscular (muscles) route. Injective doses quickly hit the target as compared to oral or topical doses.
Here’s how you can use peptide injections for arthritis:
- Mix the peptide into the bacteriostatic water and collect the required dose in the syringe.
- Clean the site with an alcohol swab.
- For subcutaneous injection, insert the needle at 45° and slowly inject the peptide dose.
- For intramuscular injection, insert the needle into the muscle at 90° and slowly release the dose.
- You must discard the used needle in the sharp container.
- You may apply slight pressure to the injection area if needed. Avoid vigorous massaging right after injection.
- Also, avoid injecting at the same point to prevent irritation.

Alternatives and Complementary Therapies for Arthritis
Following are the alternative and complementary therapies for arthritis:
- Relaxation Techniques: Tai chi and Yoga.
- Manual Therapies: Acupressure, chiropractic massage, and osteopathy.
- Herbs: Pine bark extract, ashwagandha, St John’s Wort, medicinal cannabis, and ginger.
- Supplements: Omega-3 fish oil, gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), vitamin D, and vitamin C.
- Cold and Heat Therapy: Ice packs for cold therapy. Heating pads and warm showers for heat therapy.
- PRP: Protein-rich plasma extracted from the patient’s blood and injected back.
Pro tip: Canola oil, walnuts, flaxseed oil, eggs, and oily fish (sardines, tuna, salmon, and mackerel) are rich in omega-3s. Add these items to your diet regimen to reduce arthritic inflammation. Plus, limit the intake of saturated fats.
Peptides for Joint Pain vs. Traditional Arthritis Treatments
Discover the key differences between peptides and traditional arthritis treatments below:
| Key Features | Peptides for Arthritis | Traditional Arthritis Treatments |
| Examples | BPC-157, ARA-290, collagen peptide, and others. |
|
| Mechanism | Stimulates cartilage repair and reduces joint pain and inflammation. | Reduces joint pain and inflammation and slows down the progression of arthritis. |
| Administration | Mostly injections (subcutaneous or intramuscular). | Oral form, injections, or topical creams or gels. |
| Action Onset | Peptides could take a few weeks to 3-6 months. |
|
| Side Effects | Injection site discomfort. Other side effects are usually mild and temporary. | NSAIDs can cause stomach issues and bone density loss. |
PRP vs. Peptide Therapy – Key Differences and Benefits
Now, let’s explore the key differences between peptide therapy and PRP:
| Key Features | Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) | Peptide Therapy |
| Source | PRP is collected by centrifuging the patient’s own blood. | Peptides are produced in the lab. |
| Mechanism | PRP injections contain platelets and growth factors to regenerate tissues and heal joints. | Speed up the body’s own repair mechanism by reducing inflammation and boosting collagen production and blood flow. |
| Benefits | Heals tissues, repairs cartilage, enhances injury recovery, decreases pain, and improves joint function. | Makes blood vessels, repairs cartilage, regenerates tissues, remodels bone, reduces swelling and pain, and improves mobility. |
| Treatment Approach | Everyone goes through the same procedure. | Peptide treatments are personalized. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
If you have further questions, here are the answers to some common questions below:
Is Collagen Peptides Good for Arthritis Pain?
Yes, collagen peptides are good for arthritis pain.
Research suggests that collagen peptides increase collagen to strengthen tissues, repair cartilage, lower inflammation, improve flexibility, and ultimately reduce arthritis pain.
How Long Does It Take for Peptides to Work for Joint Pain?
Peptides’ efficacy depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s health. However, peptides usually start reducing joint pain within a few weeks to 3-6 months.
Can Peptides for Rheumatoid Arthritis Reduce Flare-Ups?
Yes, peptides can reduce flare-ups and ongoing damage by decreasing inflammation, repairing cartilage, and strengthening joint tissues.
What Are the Side Effects of Peptide Injections for Inflammation?
Peptide injections may have some side effects, including pain or bruising at the injection site, stomach discomfort, and fatigue.
In rare cases, they may cause allergic reactions.
PRP vs. BPC 157 for Arthritis – Which One is Better?
Both BPC-157 and PRP show promising effects in the treatment of arthritis. PRP is usually suggested for advanced stages of arthritis.
BPC-157 is taken in mild to moderate arthritis cases. Some patients also start taking it a couple of weeks after having PRP therapy.
Conclusion
Peptides have the tendency to manage arthritis by reducing joint inflammation and enhancing tissue repair. And that’s the reason, peptide therapy is now used as a complementary treatment for arthritis.
Also, peptide therapy can be tailored to your needs. Different peptide combinations and doses are used and adjusted according to the disorder’s severity and the individual’s need. However, some peptides require further clinical testing to establish their efficacy and safety for humans.
Make sure to choose the right peptide for you after consulting with your doctor. Also, eat a nutritious and omega-3-rich diet to fulfill the deficiencies.
